The Robot Operating System (ROS) is a set of software libraries and tools that help you build robot applications.
In-depth
Nodes
The ROS graph is a network of ROS 2 elements processing data together at the same time. It encompasses all executables and the connections between them if you were to map them all out and visualize them.
Each node in ROS should be responsible for a single, modular purpose, e.g. controlling the wheel motors or publishing the sensor data from a laser range-finder. Each node can send and receive data from other nodes via topics, services, actions, or parameters.
Topics
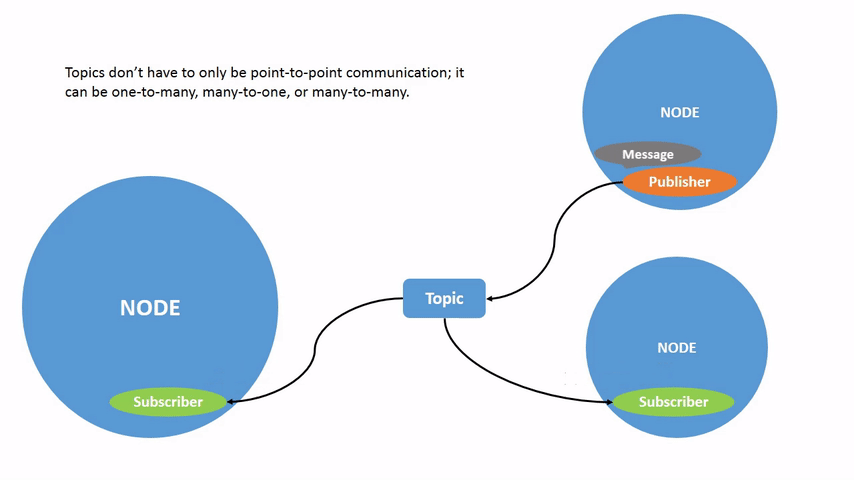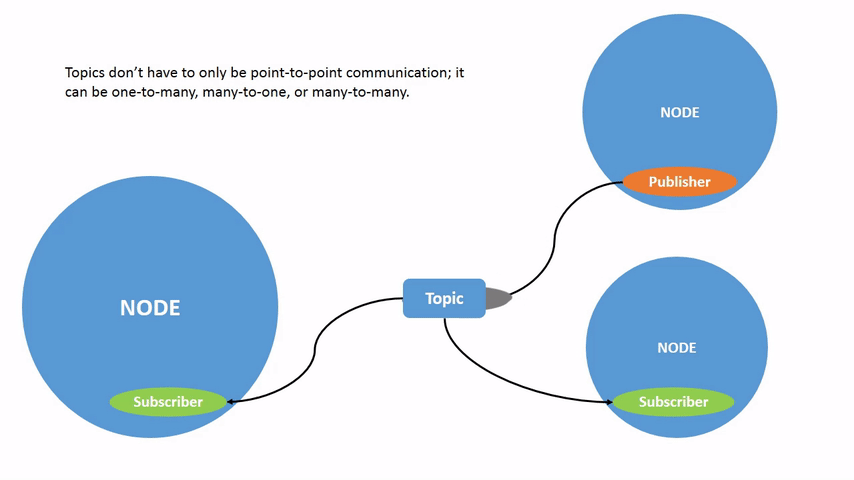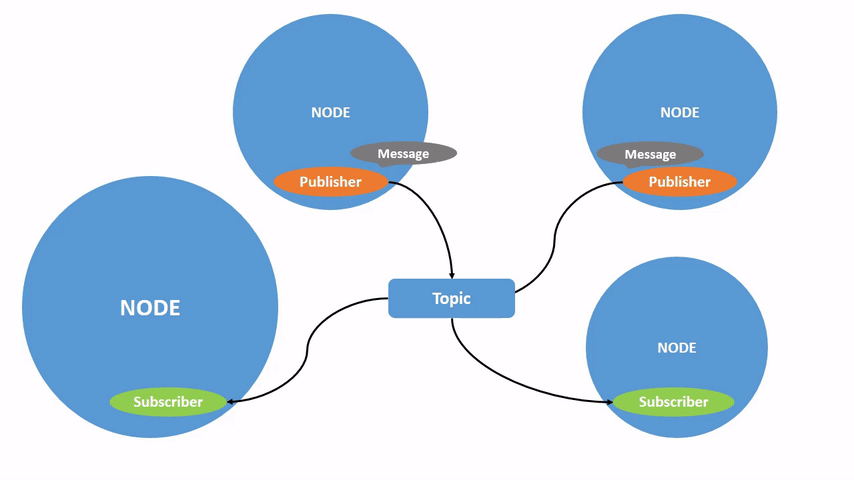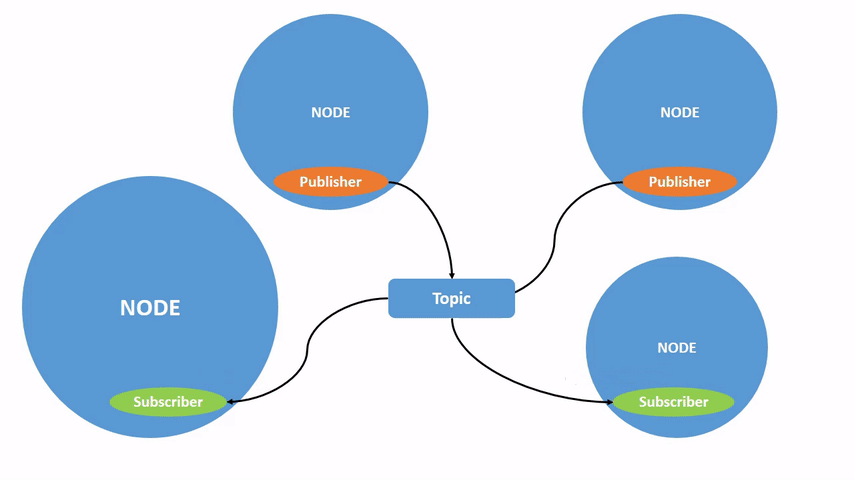
Topics are one of the main ways in which data is moved between nodes and therefore between different parts of the system. A node may publish data to any number of topics and simultaneously have subscriptions to any number of topics.
Topics have types, more commonly known as interfaces. These dictate the message format that is allowed through the topic. An example is the topic type geometry_msgs/msg/Twist, which has a message format of:
Vector3 linear
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
Vector3 angular
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
An example of a message that follows this interface is:
linear:
x: 2.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
angular:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0Services
Services are another method of communication for nodes in the ROS graph. Services are based on a call-and-response model versus the publisher-subscriber model of topics. While topics allow nodes to subscribe to data streams and get continual updates, services only provide data when they are specifically called by a client.
- Typically, nodes will have two kinds of services: ROS-specific and node-specific services. The list of ROS-specific services are:
/*/describe_parameters/*/get_parameter_types/*/get_parameters/*/list_parameters/*/set_parameters/*/set_parameters_atomically
Cheatsheets
Meta
| Purpose | Command |
|---|---|
| Run an executable | ros2 run <package_name> <executable_name> |
| Subcommand | Description |
|---|---|
launch | Run a launch file |
run | Run a package specific executable |
node | Various node related sub-commands |
topic | Various topic related sub-commands |
service | Various service related sub-commands |
action | Various action related sub-commands |
bag | Various rosbag related sub-commands |
component | Various component related sub-commands |
daemon | Various daemon related sub-commands |
doctor | Check ROS setup and other potential issues |
interface | Show information about ROS interfaces |
lifecycle | Various lifecycle related sub-commands |
multicast | Various multicast related sub-commands |
param | Various param related sub-commands |
pkg | Various package related sub-commands |
security | Various security related sub-commands |
Nodes
| Purpose | Command |
|---|---|
| List nodes | ros2 node list |
| Get info about a node | ros2 node info <node_name> |
Topics
| Purpose | Command |
|---|---|
| List topics | ros2 topic list |
| List topics with types | ros2 topic list -t |
| Get info about topic | ros2 topic info <topic_name> |
| See data being published to topic | ros2 topic echo <topic_name> |
| Publish a message to a topic | ros2 topic pub <topic_name> <msg_type> '<args>' |
| Publish the message once | ros2 topic pub --once ... |
| Get rate of data being published to topic | ros2 topic hz <topic_name> |
| Get bandwidth of data being published to topic | ros2 topic bw <topic_name> |
| List topics of given type | ros2 topic find <topic_type> |
| Subcommands | Description |
|---|---|
list | Output a list of available topics |
info | Print information about a topic |
pub | Publish a message to a topic |
echo | Subscribe to a topic and display received messages |
hz | Print the average publishing rate to screen |
bw | Display bandwidth used by topic |
find | Output a list of available topics of a given type |
delay | Display delay of topic from timestamp in header |
type | Print a topic’s type |
Services
| Purpose | Command |
|---|---|
| List services | ros2 service list |
| Get type of service | ros2 service type <service_name> |
Oddly Specific
idk what to do with this information, but it feels like these might be useful
ROS CLI
Publishing with timestamps
When publishing messages with timestamps,
pubhas two methods to automatically fill them out with the current time. For messages with astd_msgs/msg/Header, the header field can be set toautoto fill out thestampfield.
ros2 topic pub /pose geometry_msgs/msg/PoseStamped '{header: "auto", pose: {position: {x: 1.0, y: 2.0, z: 3.0}}}'If the message does not use a full header, but just has a field with type
builtin_interfaces/msg/Time, that can be set to the valuenow.
ros2 topic pub /reference sensor_msgs/msg/TimeReference '{header: "auto", time_ref: "now", source: "dumy"}'